iVenturer Foundation’s “The AI Product Landscape 2025-2026” for Business and Technology Leaders offers a strategic forecast for the AI product landscape between 2025 and 2026, highlighting the market’s shift from foundational model development to the widespread application of AI agents and integrated systems. It details explosive growth in the AI economy, particularly within large language models and AI governance, alongside a regional breakdown of investment priorities. The report further distinguishes between leading proprietary foundation models such as OpenAI’s GPT-6, Google’s Gemini, and xAI’s Grok-3, and the rise of open-weights alternatives like Meta’s Llama 3, emphasizing their respective strengths and strategic applications.
A significant portion focuses on the transformative impact of agentic AI across financial services, healthcare, and supply chain management, and also addresses the critical need for robust AI governance and security frameworks to mitigate risks like disinformation and data exposure. Finally, the text explores specialized AI products, including advancements in creative AI, enterprise productivity tools, and the emergence of humanoid robotics, concluding with actionable recommendations for business and technology leaders to navigate this evolving landscape.
Executive Summary
The artificial intelligence market is entering a new, more mature phase, defined by a fundamental shift from foundational model development to the widespread application of AI agents and integrated systems. The period from 2025 to 2026 is marked by an industry-wide transition where the primary focus is no longer on raw model performance but on the strategic deployment of AI to drive tangible business value. This evolution is evident in several key areas: a significant shift in compute spending from model training to inference, the rise of specialized AI agents that operate autonomously, and the increasing imperative of robust AI governance and security frameworks.
The competitive landscape is diversifying, with well-established players like OpenAI and Google facing stiff competition from a new generation of models, such as xAI’s Grok-3 and Anthropic’s Claude, which has gained a commanding lead in the enterprise market.1 The “open-weights” movement is also challenging the dominance of proprietary models, providing enterprises with a strategic alternative for greater control and cost efficiency.4 Across industries, AI is becoming an integral part of operations, automating complex workflows in finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.5 Simultaneously, new products in creative AI, enterprise productivity, and humanoid robotics are pushing the boundaries of what is possible.8
For technology and business leaders, success in this transformative era will depend on a multi-faceted approach. This involves prioritizing investments in agentic AI for complex workflow automation, building a secure and trustworthy AI environment, and strategically adopting a portfolio of proprietary and open-weights solutions. The most significant opportunity lies not just in technology adoption but in the strategic redesign of organizational models to empower a data-literate, AI-ready workforce, thereby leveraging human capital to its greatest advantage in an AI-powered future.
The Macro View: Market Dynamics & Investment Trends
The AI Economy: Explosive Growth and Market Projections
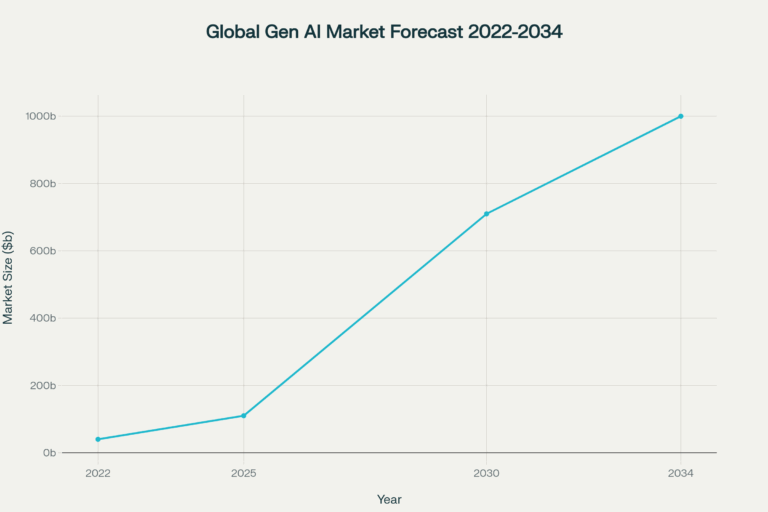
The global artificial intelligence market is experiencing a period of explosive growth, with specific segments demonstrating remarkable trajectories. The large language model (LLM) market, in particular, is forecasted to see a substantial increase in size, reflecting its rapid adoption across diverse sectors. The market was valued at USD 5.72 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 7.77 billion in 2025, with a massive long-term forecast to exceed USD 123.09 billion by 2034, accelerating at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35.92% from 2025 to 2034.12 This growth is not merely an indicator of speculative interest but a direct result of LLMs becoming a foundational technology for a wide range of applications.
In parallel, the AI governance market is also experiencing a steep growth curve. The need for robust frameworks to ensure responsible and ethical AI use is becoming a central concern for organizations globally. According to one analysis, this market was valued at USD 176,788 thousand in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2,291,494 thousand by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 37.7%.13 Another report places the 2024 market size at USD 227.6 million, with a projection to reach USD 1,418.3 million by 2030 at a CAGR of 35.7%.14 While these reports show some variation in their total market size estimations, the remarkable consistency in their growth rate projections underscores a consensus on the massive future potential of this sector. The drivers of this market are clear: the growing demand for transparency and trust in AI systems, the need to mitigate risks like bias and data privacy concerns, and a new regulatory landscape.13
Regional Investment Priorities
Spending priorities for technology executives in 2026 vary significantly by region, reflecting different market maturities and strategic focuses.15
In North America, tech decision-makers are most focused on investing in cloud, data centers, and security. The explosive use of AI is the primary catalyst for growth in cloud and data center spending, as organizations require the computational infrastructure to power their AI workloads. At the same time, high-profile security breaches and new threats, such as “bring your own AI” (BYOAI), are forcing leaders to spare no expense on security.15 A survey revealed that over 75% of executives in this region expect to grow their spending in all three of these areas in 2026.15
Europe exhibits a similar focus on cloud and security, but with a heavy emphasis on data sovereignty.15 This priority is driving investment toward private cloud and industry-specific public cloud offerings. In contrast to North America and APAC, the European market is less mature, which is reflected in a slightly lower expected growth rate for data center spending.15
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is positioned as a bold innovator, setting global trends in areas such as multilingual generative AI and humanoid robotics.15 The region is expected to see the highest rate of IT spending growth in 2026, with 88% of decision-makers anticipating budget increases, compared to 82% in both North America and Europe.16 This reflects a strategic shift from being a fast adopter of technology to becoming a primary driver of innovation.15
The Shift in Compute: From Training to Inference
A significant and strategic development in the AI market is the industry-wide shift in compute spending. The data indicates that the majority of resources are no longer being allocated to the monumental task of training foundational models but are instead shifting toward inference—the process of running these models in production.1 This is most pronounced among startups, where 74% of builders now report that the majority of their workloads are inference-driven, up from 48% just a year ago.1
This development has profound implications for the AI ecosystem. The immense capital and computational power required to train a frontier model, exemplified by initiatives like OpenAI’s Stargate I with its 5-gigawatt capacity, concentrates foundational development power in the hands of a few well-funded organizations.17 However, the shift toward inference means that the primary economic value is now being captured downstream, through the deployment and application of these models. This democratizes the AI ecosystem, allowing a wider range of companies to build high-value, AI-powered applications without the need to train their own multi-trillion-parameter models. This transition marks a maturation of the market from a research-centric phase to a value-centric one, where success is determined by practical application rather than raw compute power. The trend also explains why companies like Microsoft are heavily investing in their partner ecosystem for Copilot deployments and Azure AI solutions, as their revenue will increasingly come from inference and value-added services.18
The Core of the Ecosystem: Next-Generation Foundation Models
Comparative Analysis of the Dominant Players
The foundation model landscape for 2025-2026 is marked by intense competition and rapid evolution. Key players are differentiating their models through specialization, multimodal capabilities, and strategic positioning.
The Front-Runners
OpenAI’s GPT-6: Positioned as a multimodal, adaptive model, GPT-6 is anticipated to be released more quickly than the gap between GPT-4 and GPT-5.17 Its core focus is on becoming more flexible and useful in daily life, capable of creating chatbots that can mirror personal tastes and adapt to users.17 OpenAI’s core consumer product remains ChatGPT, and the company is working on features such as a stateful API that can remember conversation history, a feature designed to reduce repeated token costs.17
Google’s Gemini: Described as Google’s “most intelligent AI models,” Gemini is distinguished by its native multimodality, combining different types of information and generating diverse outputs from text, images, video, and code.20 The Gemini family of models is designed to cover the spectrum from speed to handling complex files, with Gemini 2.5 Flash-Lite optimized for scaled production use and Gemini Code Assist providing AI-powered assistance for developers.20 Google’s broader vision, as seen in Project Astra, is to create a conversational, real-world AI assistant that provides real-time interaction with its surroundings.22
xAI’s Grok-3: A formidable challenger, Grok-3 boasts 10 times the computational power of its predecessor, enabled by a cluster of 100,000 Nvidia H100 GPUs.3 The model is characterized by its superior reasoning abilities, supported by features like “DeepSearch” which provides transparent, step-by-step reasoning with sourced documentation, and “Big Brain Mode” which allocates extra resources for complex, multi-step problem-solving.2 Grok-3 is exclusively available to X Premium+ subscribers and is positioned to compete directly with top-tier models from OpenAI and Google in areas like logical and mathematical tasks.3
The Challenger
Anthropic’s Claude: Anthropic has strategically focused on AI safety, ethical development, and responsible deployment.23 This approach has resonated strongly with enterprises, propelling Claude to a leading 32% market share in enterprise usage, ahead of OpenAI’s 25% and Google’s 20%.1 Claude is also a top choice for code generation, capturing 42% of the market.1 Its latest model, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, is praised for its ability to handle large documents and complex coding tasks with high accuracy and transparency.23
The following table provides a clear, comparative overview of the leading proprietary models, highlighting the strategic trade-offs and competitive differentiators.
| Model Name | Parent Company | Key Differentiators | Noted Performance Benchmarks | Accessibility/Pricing Model |
| GPT-6 | OpenAI | Adaptive, personalizable chatbots; stateful API | N/A | API, ChatGPT, enterprise plans 17 |
| Gemini | Native multimodality (text, image, video, code); family of models for diverse use cases | N/A | API, Google Workspace, free tiers 20 | |
| Grok-3 | xAI | Advanced reasoning with “DeepSearch” and “Big Brain Mode”; 10x computational power 3 | MMLU: 92.7%; GSM8K: 89.3% 2 | Exclusive to X Premium+ subscribers 3 |
| Claude | Anthropic | Strong focus on safety, ethics, and truthfulness; excels at complex reasoning and long documents 24 | Leads in enterprise market share (32%) and code generation (42%) 1 | Free version, professional tiers, API 23 |
The Open-Weights Revolution
In a counter-movement to the proprietary models, a growing number of businesses are turning to “open-weights” models like Meta’s Llama 3.4 This approach is not just a passing trend but a strategic hedge against vendor lock-in and high licensing fees. Unlike proprietary systems that charge per-token API fees, open-weights models give companies access to their statistical balances, allowing them to download, customize, and deploy the models on their own cloud infrastructure without additional fees.4
This approach provides a significant level of transparency and control that closed systems cannot match. Companies can adjust the model’s inner workings to suit specific applications, a capability that is crucial for use cases involving sensitive data or for creating specialized functions like customer service or patent analysis.4 This movement is gaining considerable traction; an IDC survey found that businesses plan to use this approach for 51% of their generative AI use cases.4 The rise of open-weights models presents a viable and strategic alternative to the closed-loop, pay-per-token model, empowering a new generation of application developers and innovators.
The New Wave: Agentic AI & Its Transformative Impact
Defining the Shift: Beyond Generative AI
The evolution from generative AI to agentic AI marks a significant inflection point in the technological landscape. While generative models excel at creating content based on a given prompt, agentic AI systems go far beyond this reactive function.27 They are designed to operate autonomously, make decisions, and perform a series of actions to achieve a specific goal.27 These systems are proactive, learning from their environment and adapting to new challenges without direct human oversight.30 This capability is transforming AI from a passive tool into an autonomous agent capable of orchestrating multi-step processes and delegating subtasks to other AI models.29 The impact is predicted to be substantial; by 2028, Gartner forecasts that at least 15% of everyday business decisions will be made autonomously by AI agents, a dramatic increase from near zero in 2024.27
Revolutionizing Enterprise Workflows: The Human-in-the-Loop Era
The deployment of agentic AI is already reshaping core enterprise workflows across multiple industries, demonstrating its potential to not only automate tasks but also to fundamentally change operating models.
Financial Services: In finance, agentic AI is moving beyond simple chatbots to handle complex workflows.32 Autonomous agents are being used for internal workflow optimization, automating tasks like procure-to-pay and record-to-report.5 They can also provide real-time market tracking, with some luxury brands already using AI agents to adjust prices based on currency fluctuations to protect profit margins.5 The technology is also revolutionizing auditing, with platforms like KPMG’s smart audit platform using agents for continuous monitoring of transactions to identify anomalies and reduce human error.5 The strategic value lies in moving finance teams from reactive, end-of-week reporting to proactive, minute-by-minute responsiveness.5 One financial services VP noted their organization has 60 agentic agents in production today, with plans to deploy an additional 200 by 2026.32
Healthcare: The healthcare sector is particularly ripe for agentic AI adoption, as clinicians spend up to 70% of their time on administrative tasks.7 AI agents are automating administrative burdens such as appointment scheduling, patient data management, and follow-up care.7 The technology is also being used to streamline complex workflows like care coordination and prior authorization.30 Products like Hippocratic AI are emerging as “staffing marketplaces” where companies can hire AI agents to conduct low-risk, patient-facing services to help solve the massive healthcare staffing crisis.33 Generative AI in this sector is predicted to reduce U.S. healthcare costs by up to USD 150 billion annually by 2026, primarily through the automation of these administrative tasks.33
Supply Chain Management: In supply chain, agentic AI is acting as a “digital workforce” to enhance data quality and automate logistics.6 Agents can proactively investigate shipments, identify potential delays, and automatically coordinate with carriers and customers around the clock.6 The technology is also being used to automate supplier onboarding, eliminate manual data entry, and reduce scheduling team workload by up to 90%.6 This allows human teams to shift their focus from reactive problem-solving to proactive, end-to-end orchestration.6 The business impact is quantifiable, with the potential for a 5-10% improvement in on-time delivery and a 15-20% reduction in expedite costs.6
The following table details specific, production-level applications of agentic AI across key industries.
| Industry | Specific Use Case | Example | Business Impact |
| Financial Services | Real-time market tracking | Luxury brand LVMH uses agents to adjust prices based on currency fluctuations 5 | Protects profit margins amidst market volatility 5 |
| Healthcare | Administrative task automation | Ambient AI tools reduce documentation time by 50% 7 | Reduces clinician burnout, improves patient focus 7 |
| Supply Chain | Exception investigation & resolution | FourKites’ “Digital Workforce” monitors shipments and coordinates with partners 24/7 6 | 5-10% improvement in on-time delivery; 15-20% reduction in expedite costs 6 |
| Financial Services | Continuous audit and control | KPMG integrates AI agents into its smart audit platform 5 | Reduces human error, provides clear audit trails, and frees auditors to focus on higher-risk areas 5 |
| Healthcare | Staffing for low-risk services | Hippocratic AI provides agents to handle non-diagnostic, patient-facing services 33 | Addresses massive staffing shortages, reduces costs, and optimizes care delivery 33 |
| Supply Chain | Data quality and reordering | Agents autonomously monitor inventory levels and execute reorders 34 | Prevents out-of-stock situations and maintains consistent product availability 34 |
The Strategic Imperative: AI Governance & Security
The Looming Risks and the Need for Guardrails
The proliferation of AI systems across critical infrastructures has introduced significant new challenges and risks that require proactive management.30 Beyond well-documented concerns like algorithmic biases and data confidentiality, the pervasive spread of disinformation is a growing threat.35 AI-generated content can be intentionally misleading, and its ability to “lie through its teeth” has led the World Economic Forum to label disinformation as the biggest short-term global risk.27 The malicious use of generative models to create deepfakes and mass-produced misinformation poses a direct threat to democratic processes, public health, and corporate reputation.35
The rise of the “bring your own AI” (BYOAI) threat, identified by Forrester as a key concern for North American tech leaders, further complicates the security landscape.15 As employees adopt consumer-facing AI tools for work, sensitive corporate data may be exposed, and the lack of oversight can create new vulnerabilities.15 This necessitates a strategic move from passive, reactive security measures to preemptive governance frameworks. The future of cybersecurity in the AI era is no longer solely about technical controls; it is about establishing guardrails to detect AI-generated content and verify the authenticity of information.27
Key Products and Frameworks for Trust
To address these challenges, the market for AI governance platforms is experiencing massive growth. These platforms are designed to ensure that AI systems operate safely, reliably, and ethically by providing tools to assess potential risks, mitigate algorithmic biases, and enhance transparency.27 The value proposition of these tools is clear: Gartner predicts that by 2028, companies that use AI governance platforms will achieve customer trust scores and regulatory compliance scores that are 30% and 25% higher, respectively, than their competitors.27
While a fragmented and nascent market, it is ripe for investment and innovation. The demand for these solutions is growing as organizations across industries, from financial services to healthcare, recognize that building a secure and trustworthy AI environment is not just beneficial but essential for sustaining public and consumer confidence.14 As AI continues to integrate into the fabric of society, a robust governance strategy will become a key competitive differentiator.14
Specialized AI Products & Competitive Landscapes
The Creative AI Arms Race: Image and Video Generation
The creative AI landscape is a dynamic arena with a few dominant players setting the standard for innovation in 2025 and 2026.
Image Generation: The competition in image generation is largely a two-way battle between DALL-E and Midjourney, with each product appealing to a distinct user base. DALL-E 3 is favored for its prompt fidelity, conversational interface, and seamless integration into the ChatGPT ecosystem.8 It is the preferred tool for quick, clean, and literal image generation, making it a strong choice for businesses in marketing and IT.8
Midjourney, on the other hand, is the clear leader for high-quality, artistic, and cinematic visuals.8 With its Version 7 model, it offers sharper realism and better prompt fidelity, and it has a stronger user community, particularly in creative and tech-driven sectors.8
Video Generation: The video generation space is highly competitive, with a new generation of products offering unprecedented control and quality. Runway ML is a fan-favorite among professionals, offering a “pro-grade cinematic AI” with advanced creative controls like motion brushes.9 It excels at producing subtle, realistic, and human-like animations.39
Pika Labs is positioned as a user-friendly and fast alternative, ideal for social media and short-form content.40 A new state-of-the-art model from Google DeepMind,
Google Veo 3, is praised for its hyper-realistic video quality, integrated audio tracks, and consistent scene continuity, making it a top choice for premium agencies.9 A new and compelling entrant,
Pollo AI, wins the “crown” in some analyses by acting as a creative suite powered by multiple models like Kling AI, Runway, and Veo, offering users multi-model flexibility to switch styles with zero friction.9
The table below provides a comparative analysis of leading creative AI tools to aid in strategic decision-making.
| Product | Core Strength | Key Weakness | Best For | Noted Features |
| Midjourney | High-quality, artistic, and realistic outputs 8 | Limited legal protection, no free version 37 | Creative professionals, design, and marketing 8 | Customization tools, “Stealth Mode” for privacy 37 |
| DALL-E 3 | Prompt fidelity, user-friendly, and accessibility 8 | Can lack the “artistic feel” of competitors 8 | Beginners, quick mock-ups, and precise needs 37 | Integrated into ChatGPT and Bing, offers free access 8 |
| Runway ML | Professional-grade cinematic quality 9 | Requires more time and control for customization 40 | Filmmakers, creative directors, and professionals 9 | Motion Brush tools, advanced camera controls 9 |
| Pika Labs | Speed, user-friendliness, and dynamic movement 39 | Can suffer from distortion and less consistent results 39 | Social media creators and short-form content 40 | Fast video generation, creative and fun videos 40 |
| Google Veo 3 | Hyper-realistic visuals and integrated audio 9 | Still under development, visuals sometimes lack artistic control 9 | Premium agencies and long-form content 9 | 1080p resolution, synced audio tracks, scene continuity 9 |
Enterprise Productivity & Search
AI is fundamentally reshaping how professionals work, with a new class of tools designed to enhance productivity and information retrieval. Perplexity AI is a notable example, redefining business research by providing conversational, real-time, and fact-checked search results with inline citations.41 Case studies highlight its adoption by organizations like the U.S. Anti-Doping Agency (USADA) and deep learning company Lambda, where it has reduced research time by half and improved documentation accuracy.41 Perplexity’s business model is a freemium approach with a “Pro” tier that provides access to multiple backend models, including GPT-5 and Claude 4.0.42
On a broader scale, major technology players are embedding AI into their core productivity suites. Microsoft’s strategy for fiscal year 2026 is centered on scaling Copilot across every device and role.19 New tools like Copilot Studio and Dragon Copilot are being leveraged by partners to deliver innovative, context-aware apps and security solutions.18 Similarly,
Google is embedding its Gemini AI across its entire Workspace suite, including Gemini Advanced and the revolutionary NotebookLM Plus, an AI research assistant that helps employees make sense of complex topics.25 Gemini in Search is also designed to offer smarter and more personalized results by handling complex queries and providing curated summaries.22
Embodied AI: The Rise of Humanoid Robotics
The humanoid robotics market represents the physical manifestation of the agentic AI wave. Forrester identifies humanoid robotics as a global trend where the APAC region is becoming a “bold innovator”.15 These new products are not just hardware but are defined by their sophisticated AI systems, which enable them to perform complex, multi-step tasks in dynamic, real-world environments.
UBTECH Walker S: The Walker S is designed for industrial environments and flexible manufacturing lines.10 Standing at 1.7 meters tall, it features 41 servo joints and integrates a large language model to understand complex user intent and plan finely-tuned actions.10 Its advanced 3D semantic navigation and object detection capabilities make it a strong choice for applications requiring hand-eye coordination.10
Robot Era Star 1: The Star 1 is known for its exceptional mobility. It is described as the world’s fastest bipedal robot, with a top running speed of 3.6 m/s, or 12.9 km/h.11 The robot is powered by its proprietary end-to-end AI model, ERA-42, which allows it to master over 100 precision operations with minimal data.11 Its applications span across manufacturing, logistics, and commercial services.44
Fourier Intelligence GR-2: With 53 degrees of freedom, the GR-2 features highly dexterous, tactile-sensor-equipped hands that can recognize object shapes and materials.45 It is positioned as a versatile platform for industrial automation, healthcare, and research, capable of lifting up to 3 kg per arm.45
This convergence of sophisticated hardware and advanced AI systems marks a new era where AI is not just a digital tool but is actively changing the physical world of logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare. These polyfunctional robots represent the future of automation, capable of learning and adapting to tasks for which they were not initially programmed.27
Actionable Recommendations
Based on the analysis of the AI product landscape for 2025-2026, the following actionable recommendations are provided for technology and business leaders.
1. Prioritize Agentic AI and Workflow Automation: The analysis indicates that the most significant returns on AI investment will come from the strategic deployment of agentic AI systems. Leaders should identify and prioritize core business workflows that are currently bogged down by manual handoffs, repetitive tasks, and stale data.5 Areas like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management are prime candidates for such automation.5 The focus should be on implementing “human-in-the-loop” systems that empower human teams by freeing them from mundane tasks, allowing them to focus on high-impact projects.5
2. Secure the AI Perimeter with Governance Frameworks: As AI adoption becomes more pervasive, the risks of algorithmic bias, data exposure, and disinformation will grow.30 It is imperative that organizations implement robust AI governance platforms and security solutions to mitigate these threats.27 This includes establishing policies to manage the use of consumer-grade AI tools in the workplace and investing in solutions that can detect and protect against AI-generated misinformation.15 The goal is to build a secure and trustworthy AI environment that fosters confidence among customers and regulators.30
3. Adopt a Portfolio Approach to Model Selection: The market offers a clear choice between powerful, proprietary models and flexible, open-weights alternatives. A successful strategy for 2026 will not rely on a single solution but on a diversified portfolio.4 Proprietary models like GPT-6 and Gemini are well-suited for broad, consumer-facing applications where a large knowledge base and off-the-shelf power are required.17 Conversely, open-weights models like Llama 3 are the ideal choice for businesses that need to build highly specialized, cost-efficient applications with greater control over data and output.4 Organizations should experiment with both types of models to determine the optimal mix for their specific business and technical needs.
4. Build an AI-Ready Workforce and Redesign Operating Models: The greatest value from AI is realized when it enables a more effective workforce. Leaders should prioritize continuous, persona-based training to ensure all employees are equipped to use AI responsibly and interpret its insights.16 Moreover, a strategic focus should be placed on redesigning operating models to leverage the efficiency gains from AI. This includes reallocating at least 10% of the workforce from repetitive tasks to higher-value, more strategic roles where human judgment and creativity are a comparative advantage.15 The future of work will not be defined by technology replacing humans but by a technology-dependent care team approach, where human and artificial intelligence collaborate to achieve superior outcomes.33